Factors That Directly Impact Your Crawl Budget
1. Faceted Navigation and Infinite Filtering Combinations
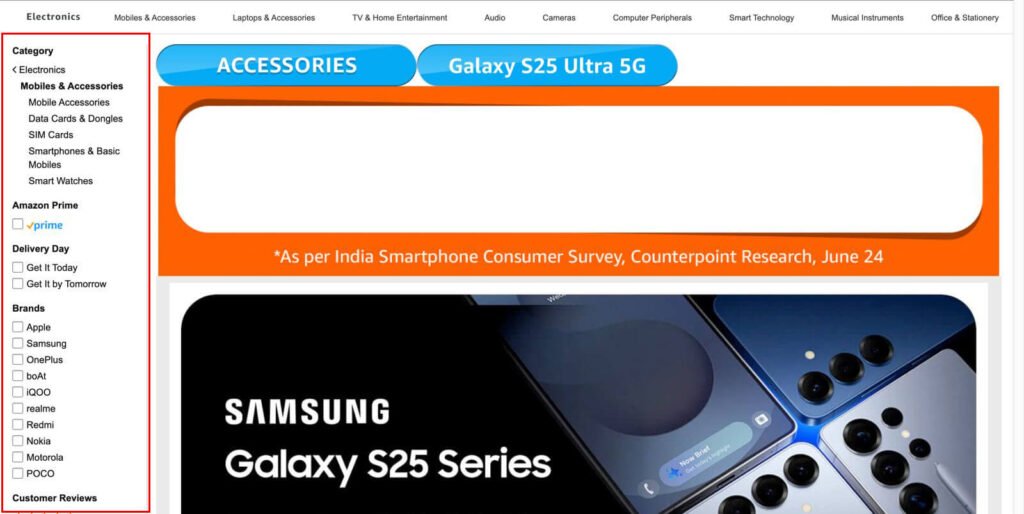
But if they also filter by “Small size,” a new URL is created:
👉 example.com/t-shirts?color=blue&size=small
How to Fix This?
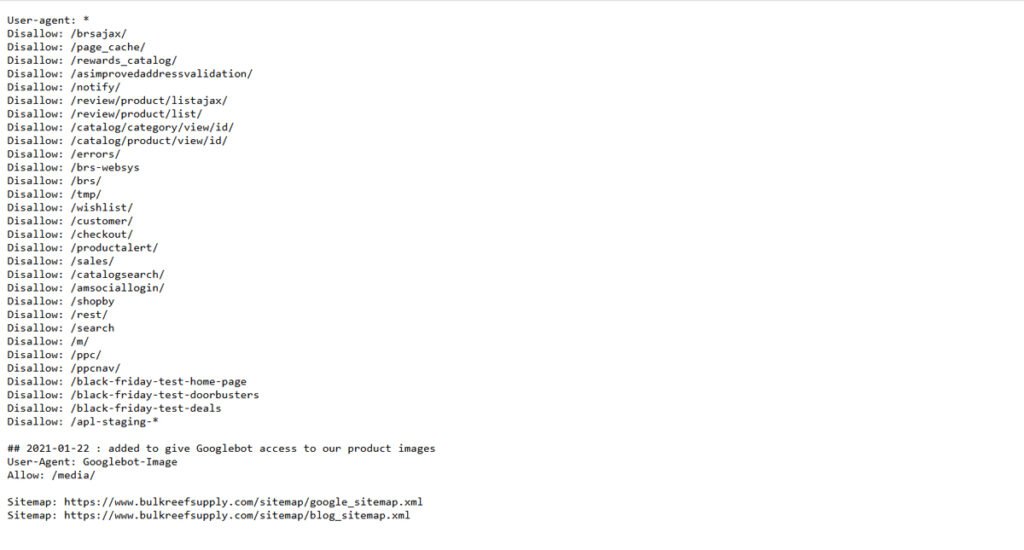
- Use Robots.txt: Block search engines from crawling filter-generated URLs so they don’t waste crawl budgets on similar pages.
- Set Canonical Tags: Tell search engines which version of the page is the “main” one, so they don’t index duplicates.
- Optimize URL Parameters in Google Search Console: This helps Google understand which filters are important and which should be ignored.
By controlling how search engines crawl your faceted navigation, you ensure they focus on your core pages—the ones that truly matter for ranking and visibility. Google provides an official guide on faceted navigation that explains best practices for managing crawl efficiency and preventing search engines from wasting resources on unnecessary URL variations.
2. Broken Links and Redirect Chains
What Are Broken Links?

What Are Redirect Chains?

1️⃣ example.com/old-page → 2️⃣ example.com/new-page → 3️⃣ example.com/final-page
Why Do These Issues Matter?
How to Fix These Issues?
- Find and Fix Broken Links: Use tools like Google Search Console or Ahrefs Site Audit to identify broken links and update or remove them.
- Minimize Redirect Chains:Ensure redirects lead directly to the final destination instead of passing through multiple steps. A 301 redirect should ideally go from old-page → final-page in one step.
- Use Internal Links Wisely: Always update internal links when URLs change to avoid unnecessary redirects or broken pages.
By fixing broken links and reducing redirect chains, you make it easier for search engines to crawl your site efficiently, ensuring they spend their time on pages that matter for search rankings and visibility.
3. Outdated Sitemaps
Think of a sitemap as a city’s official guidebook that helps tourists find the best attractions. If this guidebook is outdated, missing key locations, or listing places that no longer exist, tourists may waste time or miss important spots. The same happens when search engines rely on an outdated sitemap to crawl your website.
What is a Sitemap?
How an Outdated Sitemap Affects Crawl Budget
- Deleted pages that return a 404 error
- Pages that have moved but are still listed with the old URL
- Irrelevant pages that don’t need to be crawled
How to Fix and Maintain Your Sitemap?

- Keep Your Sitemap Updated: Whenever you add, remove, or update pages, make sure your sitemap reflects these changes.
- Submit Your Sitemap to Google Search Console: Use Google Search Console to submit or update your sitemap, helping Google understand your latest content.
- Remove Old or Broken Links: Ensure the sitemap only contains active pages to prevent search engines from wasting time on dead links.
- Use Dynamic Sitemaps for Large Websites: If your website frequently updated content, consider using an automatically generated sitemap to keep everything current.
A well-maintained sitemap ensures search engines can crawl and index your website efficiently, helping your pages show up in search results faster while making the most of your crawl budget.
4. Website Architecture
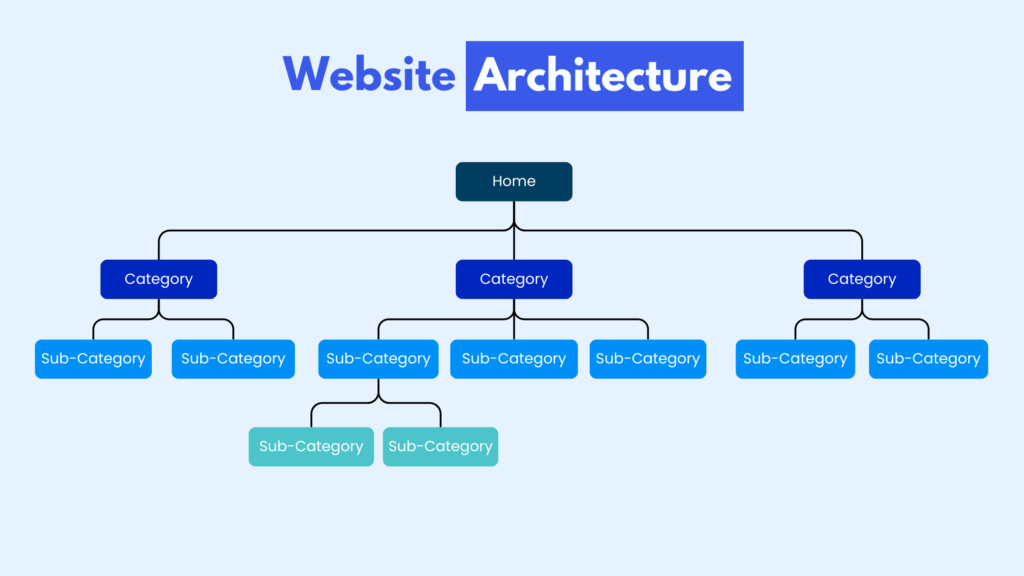
A well-structured website is like a well-planned city, where roads are clear, signs are easy to follow, and important places are easy to find. Just like a tourist who doesn’t want to waste time navigating confusing streets, search engines prefer websites with a clear and logical structure that allows them to reach important pages quickly.
Why Website Architecture Matters for Crawl Budget
If search engines have to go through too many steps, they may not reach the product page at all, meaning it won’t appear in search results.
Best Practices for Optimizing Website Architecture

- Keep Your Site Structure Shallow: Important pages should be accessible within 2-3 clicks from the homepage. Avoid deeply nested URLs that make it harder for search engines to reach key content.
- Use Internal Linking Wisely: Link to important pages within your content to help search engines discover them faster. A strong internal linking strategy acts like well-placed road signs guiding visitors and crawlers to key locations.
- Organize Categories Clearly: Whether it's a blog or an e-commerce site, make sure categories and subcategories are intuitive and easy to navigate.
- Use Breadcrumbs Navigation: Breadcrumbs act as a secondary navigation path that helps both users and search engines understand where they are on the site.
- Ensure a Mobile-Friendly Structure: Google prioritizes mobile-first indexing, so your website structure should be just as easy to navigate on a phone as it is on a desktop.
By keeping your website architecture clean and structured, you make it easier for search engines to crawl efficiently, ensuring they focus on indexing pages that truly matter for search rankings and visibility.
For more insights, check out Google’s Guide on Site Structure and SEO to understand best practices for organizing your website in a way that benefits both users and search engines.
5. Server Response Time

Imagine a search engine as a tourist trying to enter a popular attraction, but every time they reach the entrance, they have to wait in a long line before getting in. If the wait is too long, they might give up and move on to the next place. This is exactly what happens when your server response time is slow—search engines waste time waiting instead of crawling more pages.
How to Improve Server Response Time?
- Upgrade to a Better Hosting Plan: A faster, more reliable hosting service ensures your server can handle high traffic without slowing down.
- Enable Caching: Caching stores website data temporarily so that returning visitors (including crawlers) can load pages faster.
- Optimize Images and Media: Large images and videos slow down loading times. Compress images and use next-gen formats like WebP for faster performance.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): A CDN stores copies of your website on multiple servers worldwide, reducing the time it takes for search engines and users to access your content.
- Reduce Unnecessary Scripts: Too many JavaScript and CSS files can delay page loading. Minimize or defer scripts that aren’t essential for immediate display.
By improving your server response time, search engines can crawl more pages in less time, making the most of your crawl budget and boosting your chances of ranking higher in search results.
For more details, check out SiteGround’s guide on optimizing server performance which explains how to improve website speed for better crawling and indexing.
Need expert help? Check out our Website Speed Optimization Service to ensure your site runs fast and efficiently, helping both search engines and visitors have a smooth experience. 🚀
3 Factors That Control How Much Google Crawls Your Site
1. Website Authority and Popularity

Google prioritizes websites that are well-known and trusted, just like tourists naturally flock to famous landmarks instead of random side streets. If your website has high authority and is linked from other reputable sources, Google assigns it a higher crawl budget.
👉 Example: A news website like CNN gets crawled every few minutes because new content appears constantly. Meanwhile, a small blog with no backlinks might get crawled only once in a while.
🛠 How to Improve It?
- Build high-quality backlinks from trusted websites.
- Keep your website active by publishing fresh content regularly.
- Improve brand visibility through social media and PR efforts to attract more traffic.
2. Frequency of Content Updates

Google loves fresh content. If your website is updated regularly, search engines are more likely to visit frequently. Websites that don’t change much over time may get crawled less often.
👉 Example: An online store that frequently adds new products and updates descriptions will likely get crawled more often than a site that hasn’t updated its content in years.
🛠 How to Improve It?
- Update existing pages with new information to show search engines your content stays relevant.
- Publish new blog posts, product pages, or news updates consistently.
- Use Google Search Console to submit new pages and encourage faster indexing.
3. Crawl Demand (Search Engine Interest in Your Site)

Google crawls pages based on how much demand there is for their content. If people are frequently searching for topics on your site and clicking on your pages, Google will likely crawl them more often. However, if your pages don’t get much attention, Google might reduce crawling frequency.
🛠 How to Improve It?
- Optimize pages for high-demand keywords so they align with what people are searching for.
- Improve internal linking to help search engines find your important pages faster.
- Monitor Google Search Console’s Crawl Stats to see how often Google is visiting your site and look for patterns.
Final Thoughts
If you want to improve your website’s SEO and make sure Google crawls the right pages, WPService Hub offers expert technical SEO services. From fixing indexing issues to optimizing site speed and internal linking, we help ensure your website is search-friendly and performing at its best.


